Table of Contents
Ground Water Versus Aquifers: What’s the Difference?
Water is an essential resource for life, and we rely on it for everything from drinking to agriculture. But when we talk about water, we often use terms like “groundwater” and “aquifers” without fully understanding what they mean. So, to clear everything up, we’ll explore the relationship between groundwater, aquifers, and our everyday drinking water, as well as answer a few key questions, including:
● What is groundwater?
● What is an aquifer?
● Where does groundwater come from?
● What is groundwater used for?
● What is an aquifer used for?
● Is an aquifer groundwater?
What is Groundwater?
We’ll start with groundwater — what is groundwater? Groundwater is simply water that is found underground and fills the spaces between soil particles, rocks, and other materials. Groundwater can be found just about anywhere, from deep beneath the Earth’s surface to just a few feet down.
What is an Aquifer?
What is an aquifer? An aquifer is a layer of rock or sediment that contains water and can transmit it to wells or springs. Aquifers are like underground reservoirs, holding vast amounts of freshwater that can be used for drinking, irrigation, and other purposes. In fact, aquifers make up more than 95% of the Earth’s liquid fresh water (the “liquid” here is important because if we include frozen fresh water, most of it would be in frozen glaciers around the world).
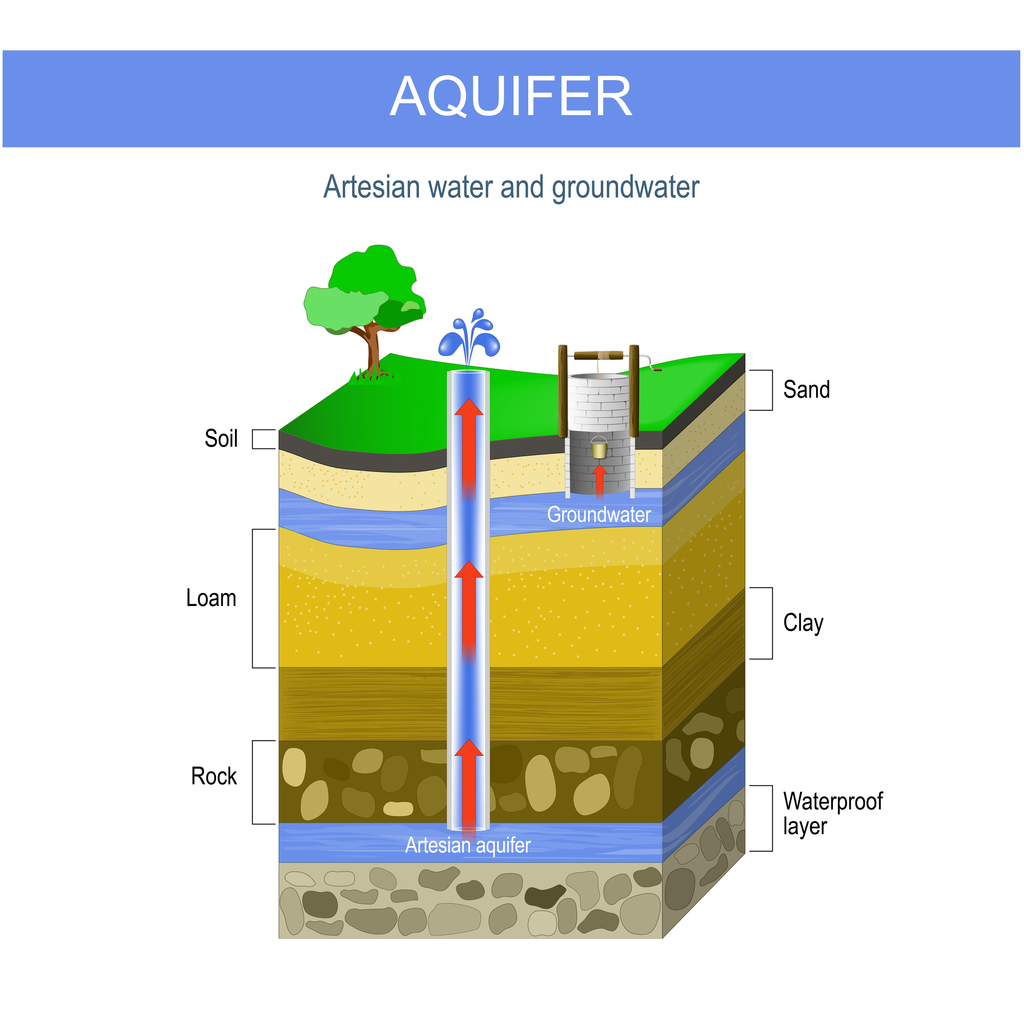
What Are Groundwater and Aquifers Used For?
To determine the difference between groundwater and an aquifer, we’ll need to answer a few questions:
What is Groundwater Used For?
First, where does groundwater come from? Groundwater comes from rain and melted snow that seeps into the ground. It serves as a source of drinking water for a large portion of the population, is used for irrigation and industrial processes, and supports environmental and geothermal energy uses.
What is an Aquifer Used For?
Aquifers are commonly used as a source of drinking water for communities, as well as for irrigation, industrial processes, and environmental uses. They are also used for geothermal energy production, where water is heated by the Earth’s core to be used for electricity generation.
Is an Aquifer Groundwater?
Not exactly, however, the answer is simple: groundwater refers to the water that’s found underground, while aquifers are the underground layers of rock or sediment that hold and transmit that water. In other words, groundwater is the water that flows through the aquifer.
The Relationship Between Groundwater, Aquifers, and Drinking Water
Groundwater is often safe to drink due to a natural purification process that occurs as water moves through the rocks and sediment — the problem is, this process can take years, so it’s difficult to ensure that groundwater hasn’t been contaminated with harmful substances like bacteria, viruses, and chemicals. Water in aquifers can be treated at purification plants, but the chlorine used in these plants can be harmful if consumed in large amounts. Furthermore, if you have corroded pipes in your home, contaminants can be added back to the water after it’s been purified at the plant.
To combat this problem, it’s essential to have a water filter in your home to remove any potential contaminants. The Life Plus water filter system from Aqua Ultraviolet achieves this result using a 3-stage sediment, carbon, and fluoride filter setup that leverages the power of ultraviolet (UV) light to break down the DNA of any bacteria or contaminants remaining in the water.
Protect Your Drinking Water with Aqua Ultraviolet
Understanding the difference between groundwater and aquifers can help us better appreciate the importance of these underground resources. By taking steps to protect our drinking water, we can ensure that we have access to clean, safe water for years to come. To protect your water, visit our Life Plus product page today.
